There are three categories of solar: customer-sited (includes residential and commercial solar), community, and utility-scale solar.
Scroll down to learn more about each.

Customer-Sited Solar
Otherwise known as "residential/commercial solar," NCSEA defines residential/commercial solar projects as solar projects installed on residential or commercial properties with the intent of supplying or off setting a portion of the customer's energy demand.
Commercial Solar: projects installed on business property with a total generating capacity of less than 2MW.
Residential Solar: projects installed on residential property.

Community Solar
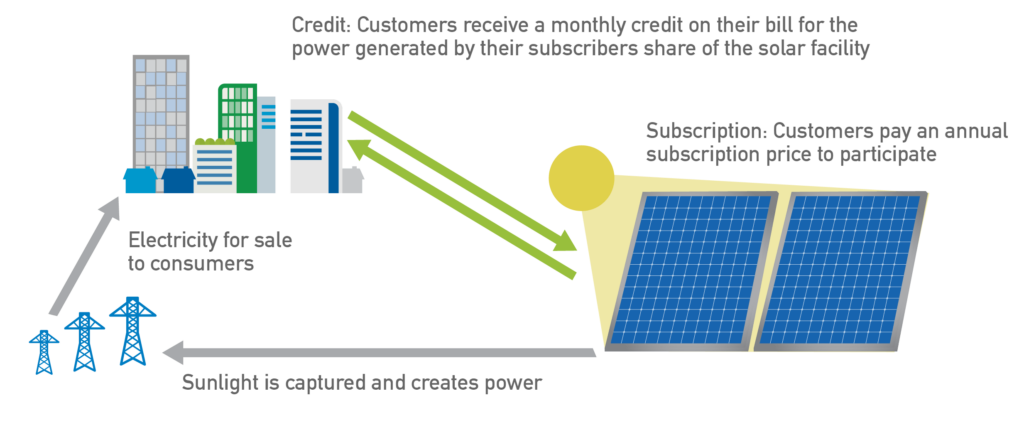
Community solar allows members of a community to share the benefits of solar without necessarily having to install solar on their property. This is a solution for households and businesses that have barriers to installing solar as they may rent, live in multi-tenant buildings, have roofs that are unable to host a solar system, or experience some other limiting circumstance.
Depending on the community solar facility organization, multiple community members can obtain financial benefit and/or power from a subscription or own a portion of the system. Community solar facilities can also be owned by utilities, co-ops, or other community organizations.

Community member financial benefit subscription, as summarized in the following diagram, is the most common community solar organization arrangement in North Carolina:
Utility-Scale Solar
Utility-scale solar includes technologies and services that convert sunlight directly into electricity through photovoltaic cells for a total generating capacity of more than 2 megawatts. This sector also includes solar thermal technologies that harness sunlight to meet thermal requirements for water or heating and cooling or create heat energy used to generate electricity for commercial or industrial purposes.
NCSEA defines utility-scale solar as solar facilities developed with the primary goal of supplying a utility with energy. This includes solar facilities that have a power purchase agreement (PPA) with a utility and solar facilities that are directly owned and operated by utilities.

Utility-scale solar power generated from ground mounted solar photovoltaic (PV) systems is growing rapidly in North Carolina. These systems utilize large areas of land, in many cases land formerly used for agricultural purposes. Using data from the US Energy Information Administration (EIA) and the investor-owned utilities (IOUs) that serve the state, NCSEA projected that even with solar providing more than 5% of North Carolina’s electricity needs, the utility-scale solar installations that generate this electricity occupy less than 0.6% of the state’s agricultural land from 2017-2030.
The map below shows all utility-scale projects currently installed in North Carolina.