Solar is captured through panels in the following ways:
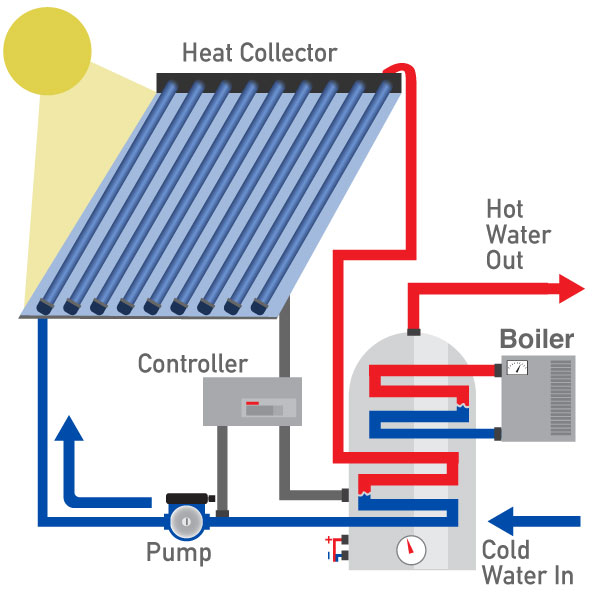
Solar Thermal Panels
Solar thermal systems use heat from sunlight for heating water used in buildings.
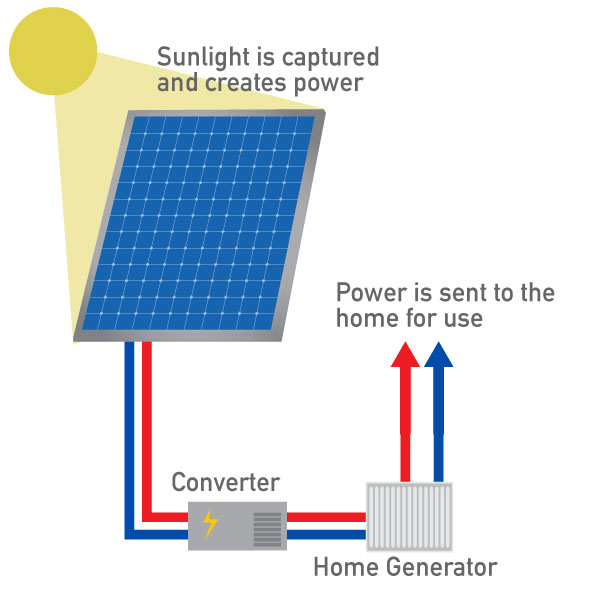
Solar Photovoltaic (PV)
Solar panels use photovoltaic cells to convert sunlight directly into electricity through a chemical reaction.
Are you a customer interested in installing solar on your roof? Visit NCSEA’s Consumer Guide to Solar Electricity to find the answers to all of your questions along with a list of reputable installers in North Carolina.
There are two ways we use solar:
Customer-Sited Solar
Customer-sited solar, which includes residential and community solar energy, includes technologies and services that convert sunlight directly into electricity through photovoltaic cells with a total generating capacity of less than 2 megawatts. This sector also includes solar thermal technologies that harness sunlight to meet thermal requirements for water or heating and cooling or create heat energy used to generate electricity for residential purposes. Customer-sited solar can be owned directly or purchased in part through a community resource or third party.

Utility-Scale Solar
Utility-scale solar includes technologies and services that convert sunlight directly into electricity through photovoltaic cells for a total generating capacity of more than 2 megawatts. This sector also includes solar thermal technologies that harness sunlight to meet thermal requirements for water or heating and cooling or create heat energy used to generate electricity for commercial or industrial purposes.

Stories of Solar in North Carolina:
Solar at NCSEA:
Solar energy not only produces clean, reliable power for customers, but also provides cost savings, community investment, and economic development opportunities throughout North Carolina. Solar represents an important piece of NCSEA’s mission to develop fair public policy that expands market access to renewable technologies. We work toward this mission every day, primarily in two key arenas.
Regulatory and Policy Work:
NCSEA leverages both regulatory and policy opportunities to ensure a free and fair future for solar energy in North Carolina. In the legislative arena our work takes several forms. NCSEA’s government affairs team lobbies to defeat efforts intended to harm the industry, limit consumer electricity choice, raise rates, and more. The team also works to advance legislation that benefits both the industry and ratepayers, and pursues state budget provisions, "stand-alone” bills, and stakeholder-driven reform packages to achieve NCSEA’s policy goals. One of the most notable energy bills to come out of recent legislative sessions was 2017’s HB589 Competitive Energy Solutions for NC, which enacted sweeping compromise reform legislation intended to open markets and bring more solar energy generation online. HB589 established several specific programs, including a process for the Competitive Procurement of Renewable Energy (CPRE), the Green Source Advantage (GSA) program for large power customers, a solar rebate program for residential customers, framework for utility-scale solar leasing practices, and guidelines for the implementation of community solar programs. Since it became law in July of 2017, NCSEA has continued to work with stakeholders and regulators to implement HB589 as intended as well as advance additional pro-solar policies.
In the regulatory space, NCSEA intervenes in various filings before the North Carolina Utilities Commission (NCUC) to protect and advance solar energy development and generation. NCSEA formally weighs in on a wide variety of regulatory matters, including IRP filings, rate cases, net energy metering, solar tariffs, and more to advance market access for and integration of solar and other renewable sources into North Carolina’s generation mix. In addition to its work in North Carolina, NCSEA also intervenes in select South Carolina solar energy before the Public Service Commission. NCSEA’s regulatory work is ongoing throughout the year and is largely informed by its legislative work.
NCSEA also seeks to advance solar energy through thoughtful storytelling and strategic communications efforts. Elaborate databases, shareable infographics, legislative district profiles, candidate education, and more propel North Carolina’s solar energy success stories through various channels to key audiences and decision-makers. These efforts not only share a compelling narrative but also provide a backdrop for the ongoing work before the NCUC and state legislature.
The federal solar investment tax credit is a tax credit that can be claimed on federal income taxes for a percentage of the cost of a solar photovoltaic (PV) system. In December 2020, Congress passed an extension of the ITC, which provides a 26% tax credit for systems installed in 2020-2022, and 22% for systems installed in 2023. The tax credit expires starting in 2024 unless Congress renews it.
In terms of eligibility, the following must apply to receive this tax credit:
- The solar PV system was installed between January 1, 2006, and December 31, 2023.
- The solar PV system is located at an individual’s primary or secondary residence in the United States, or for an off-site community solar project, if the electricity generated is credited against, and does not exceed, your home’s electricity consumption.
- The solar PV system is owned by the individual claiming the tax credit
- The solar PV system is new or being used for the first time.
Are you a North Carolina resident trying to install solar on your home or property, but having difficulty with your Home-Owners Association (HOA)? NCSEA wants to hear from you.
Net Energy Metering:
Net energy metering (NEM) is a billing system that credits residential and commercial customers for any excess electricity that they generate and sell back to the utility from the grid. For the latest status update on net metering in North Carolina, including the latest "Solar Choice Net Metering" agreement, visit our NEM webpage.
"If we're going to meet the challenge of our generation to rapidly transition our energy grid to renewables, we need to accelerate the deployment of rooftop solar in NC as a viable, affordable way to produce clean, distributed energy. NCSEA works tirelessly to support our industry by helping us overcome obstacles and barriers thrown up by those with vested interests in the status quo, so that we can continue the important work of changing our energy landscape."
- Doug Ager, CEO and Co-founder, Sugar Hollow Solar

Looking Ahead for Solar:
Our goals in the solar space are ever-changing based on the political and regulatory landscapes, but our overarching mission remains the same: ensure fair policies and market access for solar energy companies in North Carolina. In addition to our current regulatory goals, our legislative agenda outlines specific policy goals NCSEA is working toward this legislative session.